Friction welding provides a high-strength, cost-effective solution to join two workpieces together. The result is complete metal fusion without the need for fluxes, fillers, gasses, or an external heat source. The solid-state process requires minimal joint preparation and eliminates the possibility of porosity or slag inclusion. The narrow heat-affected zone of the weld area protects the molecular integrity of both components. This bonding method offers consistent and repetitive results with faster production turn-around. Cost savings result by reducing the amount of raw material, machining, and tooling required to produce a completed part. Design flexibility provides turbine construction from one metal and shaft selection from a lower cost stock or vice versa. The joining of dissimilar metals is possible where conventional methods may not work.
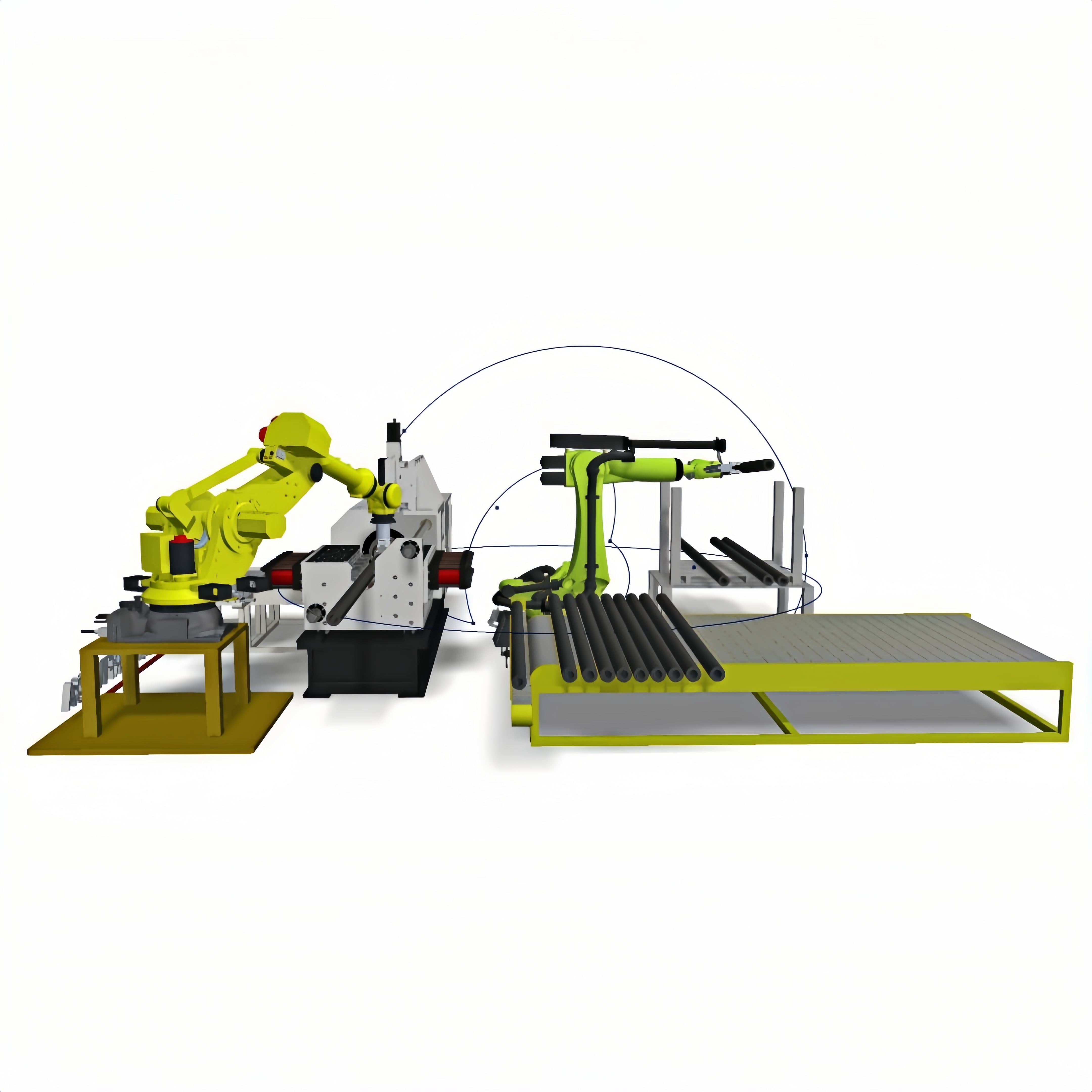

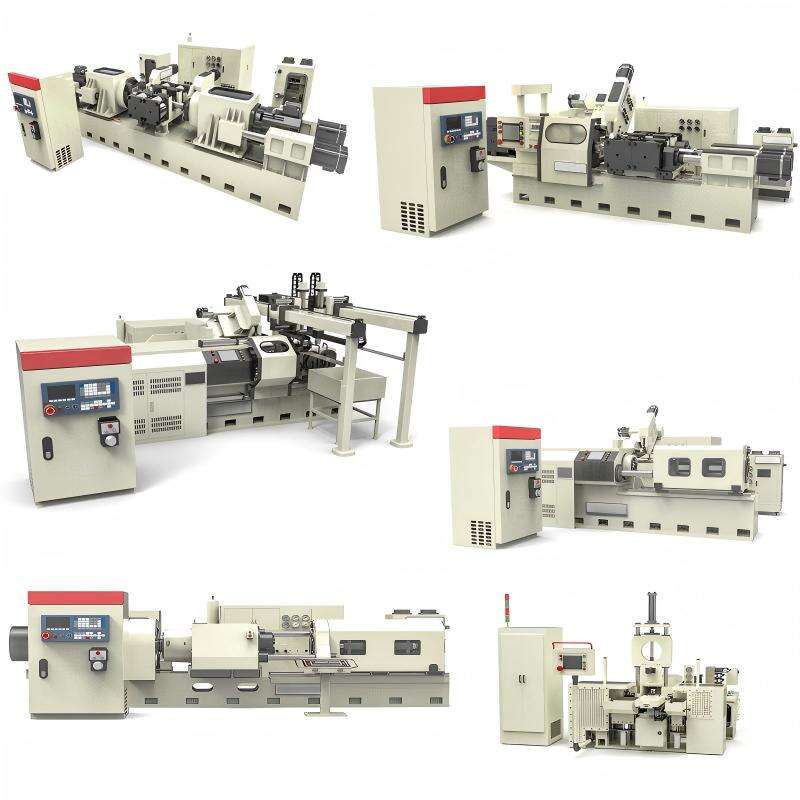
Product brief
Friction welding provides a high-strength, cost-effective solution to join two workpieces together. The result is complete metal fusion without the need for fluxes, fillers, gasses, or an external heat source. The solid-state process requires minimal joint preparation and eliminates the possibility of porosity or slag inclusion. The narrow heat-affected zone of the weld area protects the molecular integrity of both components. This bonding method offers consistent and repetitive results with faster production turn-around.
Cost savings result by reducing the amount of raw material, machining, and tooling required to produce a completed part. Design flexibility provides turbine construction from one metal and shaft selection from a lower cost stock or vice versa. The joining of dissimilar metals is possible where conventional methods may not work.
Product Description
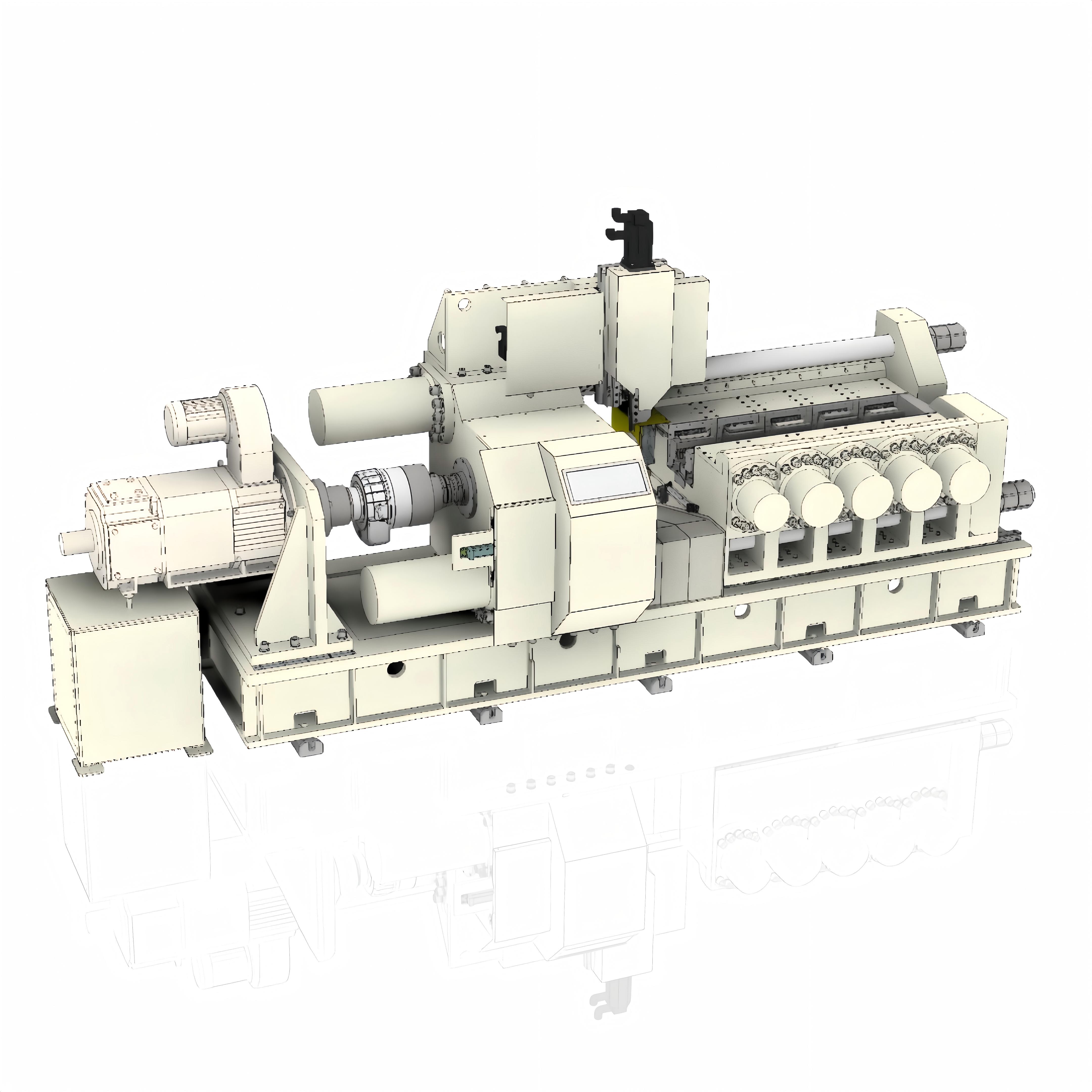
Direct Drive friction welding can be an attractive technology because we can customize the parameters to achieve our desired results.
For example, if we are welding a hardenable steel, we can apply some extra heat by using a longer second friction phase in order to help control the cooling rate.
In Direct Drive, we have a spindle limitation of the thrust bearing’s ability to react forge load when rotating, so typically we need to decrease our spindle speed to zero before we can bring on the forge load. At this point we increase to full forge load, squeeze out all of the softened material, and complete the weld.
Following are a few of the significant applications of this technology:
Product parameters
| Model | Max.upset force(KN) | Max.welding area(mm) | Welding dia. | Speed(rpm) |
| DBS-2 | 20 | 20-140 | 5月13日 | 5000 |
| DBS-5 | 50 | 50-260 | 8月18日 | 3000 |
| DBS-12 | 120 | 150-700 | 14-30 | 1500 |
| DBS-20 | 200 | 150-1020 | 14-36 | 1500 |
| DBS-30 | 300 | 314-1600 | 20-45 | 1200 |
| DBS-40 | 400 | 500-2400 | 25-55 | 1100 |
| DBS-63 | 630 | 960-3400 | 35-64 | 1000 |
| DBS-80 | 800 | 1300-5000 | 40-75 | 950 |
| DBS-100 | 1000 | 1600-6000 | 45-86 | 890 |
| DBS-125 | 1250 | 2000-7800 | 50-100 | 600 |
| DBS-160 | 1600 | 4300-8792 | 89-160 | 580 |
| DBS-200 | 2000 | 5100-12500 | 102-189 | 500 |
| DBS-250 | 2500 | 3850-15500 | 70-140 | 500 |
| DBS-320 | 3200 | 6400-20000 | 90-160 | 380 |
| DBS-400 | 4000 | 8000-25000 | 100-180 | 350 |
| DBS-500 | 5000 | 8000-31400 | 100-200 | 320 |
| DBS-700 | 7000 | 8000-44000 | 100-240 | 320 |
